23.07.2019
July 2019 – AC Power Relays are enabling efficient EV Chargers and Other Green Energy Systems
Published on: 23/07/2019
AC power relays play an important role in the adoption of EV charging stations
Increasing the number of charging stations in Europe to 500,000 by 2025 is one of the EU’s goals under the “Clean Power for Transport” program. In 2001 there was just 12,000 charging stations across the continent and since each charging point requires multiple relays in it’s design, the adoption of electric vehicle chargers is a major opportunity for manufacturers and distributors of power relays.
Electric vehicle station regulations
IEC 61851-1 defines the Electric vehicle conductive charging system which establishes general characteristics, including charging modes and connection configurations, and requirements for specific implementations of both electric vehicle (EV) and electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) in a charging system. The IEC sets out the connectivity and wired charging mode requirements nominally 16A. Due to the fact the DC supplied is AC derived, fault detecting is mandatory and explained in IEC 62752 for in-cable control and protection devices for mode 2 charging of electric road vehicles (IC-CPD) and this protection is usually provided by a Residual Current Device (RCD).
IEC6066-1 describes the insulation coordination for equipment (creepages and clearances) within low-voltage EV Charger systems. This standard defines three charger modes with different charge currents, charge durations and complexity of installation.
The mode 1 charging station (16A) is the easiest install and is compatible with ordinary household electrical outlets but also the slowest and takes 8 hours to provide around 40 miles of charge. The mode 1 stations do not have an internal AC/DC converter but provide AC energy which is rectified in the vehicle’s on-board charging system. They can be plugged directly into regular residential outlets and installed in the home without professional assistance because of their low current.
Mode 2 charging stations (16A, at 3 phase 32a max) use a IC-CPD (In Cable Protecting Device) which controls the charging and connecting progress as well as the switch off in case of failure. The maximum charging current is limited by the IC-CPD and the charging time is the same as mode 1 at 16A.
The mode 3 charging stations (3 phase 32A) are able to communicate with the car and control the maximum charging current. The typical maximum AC charging current is 32A, it has a fixed connection to the electrical installation., charging time is reduced to approximately 1.5 to 2 hours dependent on battery capacity. Mode 3 stations are commonly used in homes, factories and offices and need to be installed by electricians who full understand the installation and connection regulations.
Mode 4 charging stations are typically a DC charger where the maximum DC charging current is handled by the charging station directly instead of being done inside the car. Mode 4 charging stations will be installed on highways where cars need to be charged quickly, they take 20-30 minutes to charge the vehicle up to 80% of its capacity.
AC Power Relays
An AC latching relay may be used to allow load switching is done under safe conditions minimising stress on all components. An AC latching relay is often used in each AC supply line in to the converter. The relays must cut off the circuit to prevent any abnormal currents that occur from affecting the commercial power supply. Power relays are required as a safety measure to protect the power supply system.
Manufacturers understand that the switching device to connect and disconnect the electricity supply system is one of the most demanding relay applications in common use, this is due to the very high current and voltage levels required for absolute reliability and safety. Manufacturers are now introducing power relays for this purpose, offering a high switching capacity in a compact size. An AC power relay with low contact resistance below 3mΩ and a low switching power of 350Mw or less is ideal. The best solution is a latching relay, it remains in the closed position for the entire period of the change without consuming further power and can hen be opened with a further brief current pulse.
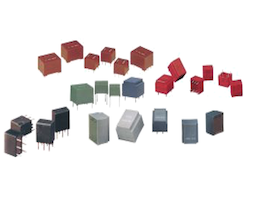
GD Rectifiers is an authorised distributor for IXYS Integrated Circuits Division now owned by Littelfuse offering a wide range of power relays designed to switch power reliably to high current loads under the control of milliamp-level DC signals. IXYS’ wide range of blocking voltages and current handling capabilities offer flexible design options. IXYS’ range of power relays are available in two types of packages: bidirectional (AC/DC) and unidirectional (DC only). Power relays are commonly used in: industrial controls, motor controls, robotics, transportation equipment, aerospace and defense.
Bidirectional power relays are designed to switch high current loads and current flows in both directions. View the full range of IXYS’ bidirectional power relays here.
Undirectional power relays are designed to switch high current loads where current flows in only one direction. View the full range of IXYS’ unidirectional power relays here.
For further information on power relays or to receive a quote, please call: 01444 243 452 or email: enquiries@gdrectifiers.co.uk.